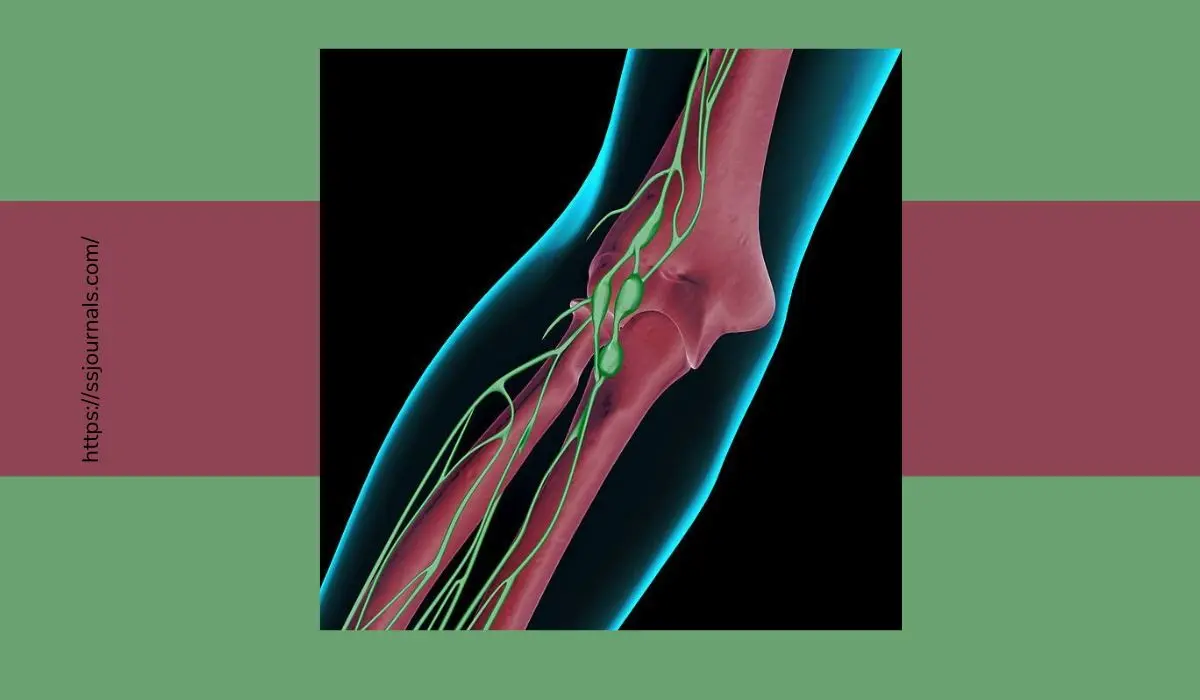
The lymphatic system is a vital part of the immune system. It contains lymphatic vessels and lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, and thymus gland. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped glands located throughout the body along the lymphatic system.
They act as filters for the lymph fluid, removing bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. Lymph nodes can become swollen due to infection, inflammation, or cancer. One group of lymph nodes located in the upper arm near the elbow is called the epitrochlear lymph nodes.
What Are Epitrochlear Lymph Nodes?
Epitrochlear lymph nodes are a small group of usually 1-4 lymph nodes found along the medial side of the upper arm near the elbow. ‘Epitrochlear’ refers to their location near the epitrochlea region of the humerus bone, which is the bony projection on the inner side of the elbow.
Epitrochlear nodes drain lymph fluid from the upper limb, as well as receive drainage from the axillary (armpit) nodes. Along with the axillary nodes, they are one of the first filtration points for lymphatic vessels draining from the breasts, arm, and shoulder region.
Due to this anatomy, swollen or enlarged epitrochlear lymph nodes can be an important indicator of infections, injuries, or metastatic cancers in areas like the hand, arm, breast, and upper body that drain into these nodes.
Epitrochlear Lymph Node Anatomy
Epitrochlear nodes are classified as distal extremity lymphatics that primarily drain the upper limbs. There are usually between 1-4 epitrochlear lymph nodes that form a chain along the medial bicipital groove between the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles in the upper arm.
The medial anterior cubital lymph nodes are also sometimes included in the epitrochlear group. Epitrochlear nodes receive afferent lymphatic vessels that drain lymph from the arm, forearm, shoulder, and lateral thorax below the level of the axilla.
Efferent lymphatic vessels from the epitrochlear nodes lead to the central axillary nodes or directly to the subclavian lymphatic trunks.
Epitrochlear nodes are clinically significant because their position allows cancers of the hand, arm, breast, and thorax to metastasize to these lymph nodes and cause them to become enlarged, hardened, or tender.
This makes examination of the epitrochlear lymph nodes an important diagnostic step when suspicion of cancer in the arms, thorax or breasts is present.
Also Check: What Is Myositis Ossificans? Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Causes Of Swollen Epitrochlear Lymph Nodes
There are several potential causes of enlarged or swollen epitrochlear lymph nodes including:
➜ Localized Infection
Bacterial or viral infections of the hand, arm, shoulder, or chest can cause proximal lymph nodes like the epitrochlear group to reactively enlarge as they filter out infectious agents. Common causes include skin infections like cellulitis or abscesses, upper respiratory infections, or tissue injuries leading to infection.
➜ Inflammatory Conditions
Autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus may cause generalized lymph node swelling throughout the body, including the epitrochlears.
➜ Metastatic Cancers
Cancers originating from the breast, lungs, thyroid, bones and other tissues can metastasize and spread via the lymph nodes causing epitrochlear enlargement. Breast cancer metastases are most common. Enlarged hard epitrochlear nodes may be the first symptom that leads to cancer diagnosis.
➜ Lymphomas
Cancers of the lymphatic system itself most commonly non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas may affect lymph node groups like the epitrochlears. This can present as uniform enlargement of nodes.
➜ Lipoma
A benign fatty tumor near a lymph node can push on and compress local nodes like the epitrochlears making them palpably enlarged.
➜ Cat Scratch Disease
An infection with the bacteria Bartonella henselae, often acquired from a cat scratch or bite, can cause tender, swollen regional lymph nodes like the epitrochlear group.
Other general causes of localized lymphadenopathy like tuberculosis infections or melanoma may also rarely affect epitrochlear lymph nodes.
Other general causes of localized lymphadenopathy like tuberculosis infections or melanoma may also rarely affect epitrochlear lymph nodes.
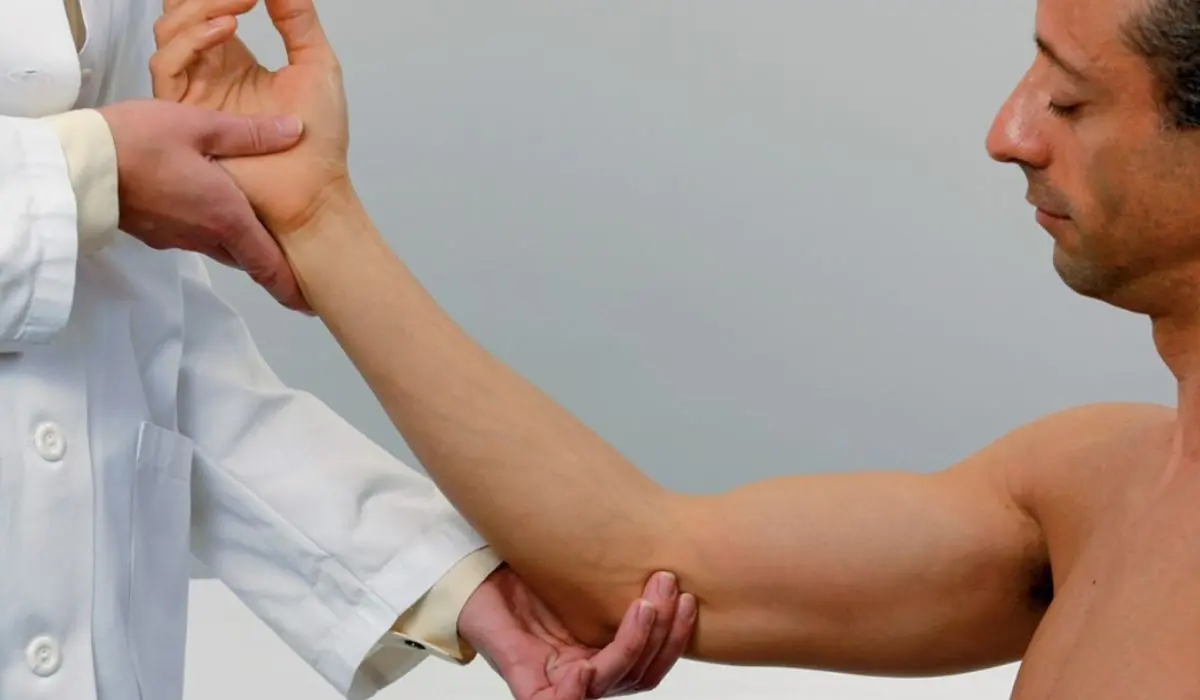
Diagnosing Swollen Epitrochlear Lymph Nodes
If swelling in the epitrochlear region is noted, further examination and testing should follow to determine the underlying cause, including:
- Medical History to identify risk factors like cancers, infections, or inflammatory conditions that could be related. The presence of systemic symptoms is noted.
- Physical Exam to palpate and characterize enlarged nodes – noting size, shape, consistency, mobility, tenderness, and warmth. Other localizing signs are identified.
- Imaging Tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the internal structure of nodes and characterize abnormalities. This can help distinguish enlarged nodes from lipomas for example.
- Biopsy of Nodes for microscopic examination and tissue diagnosis if infection, cancer or lymphoma is suspected. Excisional biopsy is often required.
- Bloodwork to look for biomarkers indicative of cancers, inflammation, or infections that could be related. A basic metabolic panel and blood counts are routine.
Once a diagnosis is reached, proper treatment can commence – this may include antibiotics for infections, chemotherapy and radiation for cancers, immunosuppressants for inflammatory conditions, or periodic monitoring for benign self-limited causes. Consultation with specialists in oncology, infectious disease or rheumatology is sometimes needed.
Conclusion
Though small in size, the epitrochlear lymph nodes that reside in the upper arm can provide important clues to disease processes in the arm, chest, breast and body.
Careful clinical examination and investigation of enlarged epitrochlear nodes can facilitate early diagnosis and treatment of conditions ranging from localized infections to widespread metastatic cancers.
Anatomical knowledge of epitrochlear nodal drainage patterns assists practitioners in considering associated cancers and using node biopsy for tissue diagnosis when needed.
FAQ
Epitrochlear lymph nodes are located in the medial upper arm near the elbow, adjacent to the epitrochlea region of the humerus bone. They form a chain in the bicipital groove between the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles.
Epitrochlear nodes drain lymph fluid from the upper extremity including the hand, forearm, arm and shoulder as well as the lateral thoracic wall below the axilla.
Common causes of swollen epitrochlear lymph nodes include infections of the arm or hand, inflammatory conditions, metastatic cancers from the breasts, lungs or thyroid, lymphomas, and localized lipomas. Enlarged epitrochlears may be tender, hardened, or fixed to surrounding tissues.
Evaluation includes a clinical exam noting node characteristics, imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans, bloodwork, and sometimes biopsy of the lymph node for microscopic diagnosis. Findings are correlated with the patient’s medical history.
Epitrochlear lymph node enlargement can be the first presentation of underlying cancers like breast cancer that have metastasized to these lymph nodes. Swelling can also indicate local infections or inflammatory conditions that need to be treated. Careful evaluation of abnormal epitrochlear lymph nodes is important.
More: Cause Of Right Side Chest Pain – Factors Causing Chest Pain!