Dry eye syndrome, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is a common condition affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the tears fail to adequately lubricate the surface of the eye, causing irritation, redness, stinging, and blurred vision.
There are various causes of dry eye, including aging, autoimmune disorders, medication side effects, and environmental factors. Chronic dry eye can impair the quality of life and routine daily activities. Fortunately, there are many effective self-care methods that can provide symptomatic relief and help manage this troublesome condition.
What Is Dry Eye Syndrome?
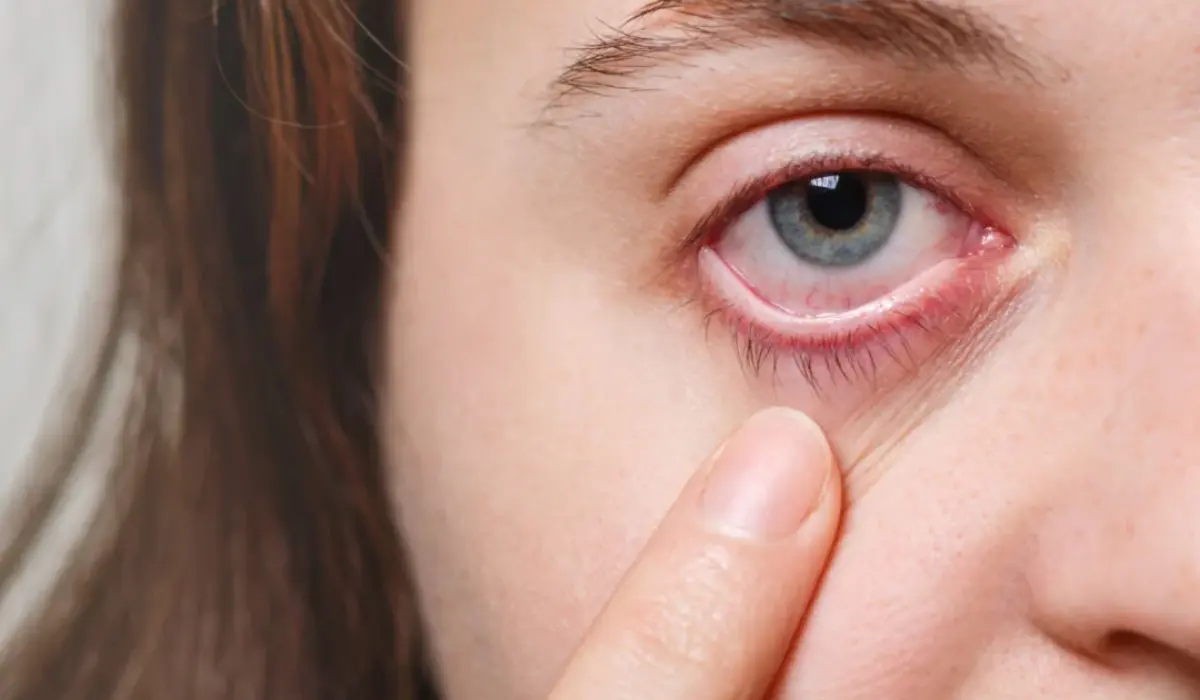

Dry eye syndrome is a multifactorial disease of the ocular surface characterized by insufficient tear production or excessive tear evaporation. This results in discomfort and visual disturbances due to the drying of the conjunctival and corneal surfaces.
Tears play a critical role in lubricating the eyes and providing nutrients essential for ocular health. They are composed of a mixture of oils, mucus, and water. The lacrimal glands, meibomian glands, goblet cells, and accessory glands all contribute to tear production, secretion, and regulation of tear film stability.
When any part of this system is compromised, it can lead to rapid tear evaporation and drying of the surface of the eye.
There are two major types of dry eye – aqueous deficient and evaporative. Aqueous deficient dry eye is caused by impaired lacrimal gland secretion. Evaporative dry eye occurs when meibomian glands in the eyelids fail to produce a healthy lipid layer, leading to excess evaporation of tears.
Symptoms can range from mild intermittent irritation to chronic inflammation with permanent damage if left uncontrolled. Diagnosis is made by an eye care professional based on a slit lamp examination, patient history, and specialized dry eye tests. Treatment aims to restore moisture, reduce inflammation, and address the underlying cause.
Effective Ways To Manage Dry Eye Syndrome
While dry eye requires professional treatment, there are many beneficial self-care techniques that can provide relief and support ocular health. These include:
Warm compresses – Applying a clean warm washcloth to closed eyes for 5-10 minutes melts meibum in blocked gland ducts to improve tear quality. Do this 2-3 times daily.
Cool compresses – Placing refrigerated eye masks or damp cool cloths over closed eyes can alleviate burning and soothe inflamed eyes.
Artificial tears – Frequent use of preservative-free lubricating eye drops replenishes moisture and washes away irritants. Carry a bottle for use as needed.
Lid hygiene – Gently scrubbing the eyelid margins with a clean wet cloth removes debris and unblocks glands.
Humidifiers – Adding moisture to indoor air prevents tear film from rapidly evaporating.
Omega-3s – Oral supplements with EPA/DHA support tear production and reduce dry eye inflammation.
Diet – Eating foods rich in omega-3s, vitamins A, C, and E, zinc, and antioxidants can improve ocular health.
Reduce screen time – Take frequent breaks from digital devices and avoid exposure to dry air when using.
Ocular massage – Applying light pressure on closed lids increases meibum secretion.
Sleep masks – Wearing moisture-retaining masks at night prevents tear evaporation during sleep.
Allergy management – Controlling environmental allergies can minimize ocular surface irritation.
Smoking cessation – Quitting smoking alleviates smoke-induced dry eye symptoms.
Along with self-care, it is essential to follow the treatment plan outlined by your eye doctor, which may include prescription medications. With a holistic approach combining professional treatment and self-care techniques, dry eye can be effectively managed for better eye comfort and vision.
Final Take
Dry eye syndrome is a troublesome condition stemming from inadequate tear quantity or quality that disrupts ocular surface health. A multifaceted self-care approach is an important aspect of managing this chronic disease.
Methods like warm compresses, artificial tears, dietary changes, hydration, eyelid hygiene, and avoiding irritants can provide symptomatic relief and improve tear production and stability.
By implementing self-care techniques recommended by eye care providers as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with dry eye can keep their eyes lubricated, reduce inflammation, and maintain their vision and quality of life. Consistent self-care is key to successfully controlling dry eye syndrome.
FAQ
Yes, uncontrolled dry eye syndrome can lead to permanent corneal scarring, ulceration, and vision loss over time. That’s why it’s critical to seek a professional diagnosis and follow treatment recommendations.
Use artificial tears as often as needed to obtain relief and maintain moisture, which can range from 2-10 times per day for moderate dry eye. Severe dry eye may require lubricating drops every 1-2 hours. Always follow product instructions.
Home remedies like warm compresses, eyelid scrubs, and humidifiers can provide symptomatic relief but not treat the root causes of dry eye. See an optometrist or ophthalmologist for diagnosis and medical treatment. Self-care complements but does not replace professional dry eye treatment.
Yes, contact lens wear can exacerbate dry eye symptoms by interfering with tear film stability. Switch to daily disposable lenses, use rewetting drops, take frequent breaks, and discuss other options with your eye doctor.
Yes, contact lens wear can exacerbate dry eye symptoms by interfering with tear film stability. Switch to daily disposable lenses, use rewetting drops, take frequent breaks, and discuss other options with your eye doctor.