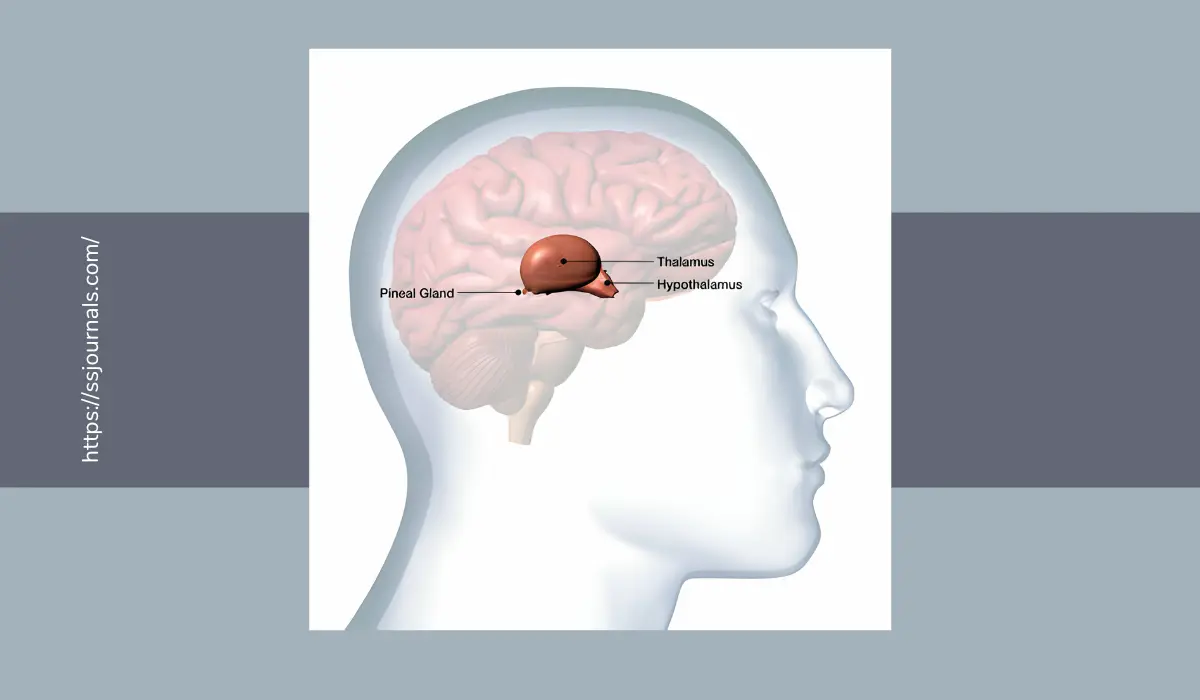
The pineal gland, often referred to as the “third eye-brain,” has captivated both scientific and spiritual communities for centuries. This small, pine-cone-shaped endocrine gland, located deep within the brain, has been the subject of numerous theories and beliefs, bridging the realms of science and spirituality fascinatingly.
What does the pineal gland look like?
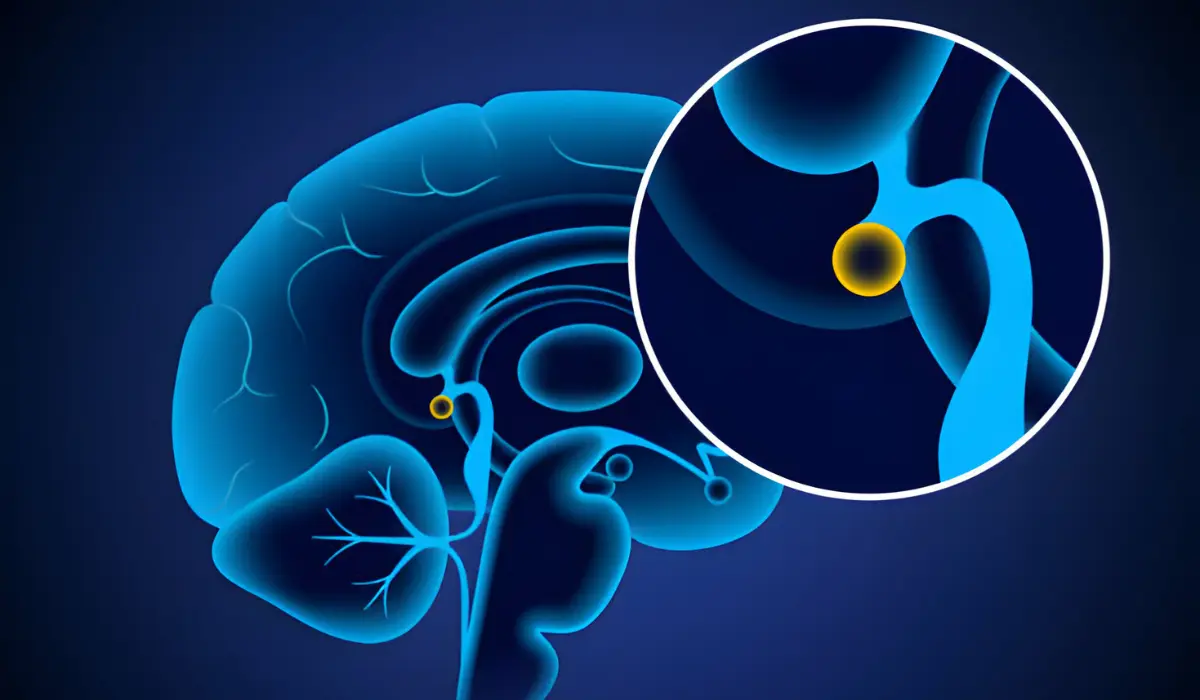
The pineal gland, also known as the “pineal body,” is a tiny, reddish-gray structure that resembles a pine cone. It measures approximately 6-8 millimeters in length and is situated near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, just above the brain stem.
Pineal gland secretes
The pineal gland is responsible for producing and secreting the hormone melatonin, which plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s sleep-wake cycles, known as circadian rhythms. Melatonin is also believed to have antioxidant properties and may contribute to overall well-being.
Pineal body
The pineal body, or the pineal gland, is considered a neuroendocrine transducer, meaning it can convert neural signals into hormonal signals and vice versa. This unique function allows the pineal gland to integrate information from the body’s nervous system and the endocrine system, making it a crucial link between the two systems.
The pineal gland in humans
In humans, the pineal gland is believed to play a pivotal role in various physiological processes, including sleep regulation, hormone production, and even the onset of puberty. Its location and function have led many cultures and belief systems to associate it with spiritual enlightenment, intuition, and the “third eye.”
Pineal eye human
While the pineal gland is often referred to as the “third eye,” it is important to note that it is not a literal eye in humans. However, in certain reptiles, amphibians, and some other lower vertebrates, the pineal gland is a light-sensitive organ, resembling a rudimentary eye, known as the “pineal eye” or the “third eye.”
Pineal gland
The pineal gland has been a subject of fascination for millennia, appearing in various ancient texts and belief systems. In Ancient Egypt, it was associated with the “Eye of Horus,” a powerful symbol of protection, good health, and spiritual awakening.
What is the pineal gland?
The pineal gland is a small, pea-sized endocrine gland located in the brain’s epithalamus, near the center of the brain. It is often referred to as the “third eye-brain” due to its unique location and its role in regulating various bodily functions, as well as its spiritual and metaphysical associations.
Pineal body function
The primary function of the pineal body is the production and secretion of the hormone melatonin. Melatonin plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s circadian rhythms, or sleep-wake cycles, by responding to light and dark cues from the environment. Additionally, the pineal gland is believed to be involved in regulating other physiological processes, such as immune function, reproductive hormones, and even the onset of puberty.
3rd eye gland
The term “3rd eye gland” refers to the pineal gland’s spiritual and metaphysical associations. In many ancient cultures and belief systems, the pineal gland was believed to be the seat of the soul or the gateway to higher consciousness and spiritual awakening. This belief stemmed from its unique location and function within the brain, as well as its potential light-sensing capabilities in certain animals.
Bottom Line
The pineal gland, or the “Eye of Horus,” as it was known in Ancient Egypt, has captivated the human imagination for thousands of years. Its unique position and function within the brain have made it a bridge between science and spirituality, offering a glimpse into the complex interplay between the physical and metaphysical realms. As research continues to unravel the mysteries of this fascinating gland, its significance in both the scientific and spiritual domains continues to be explored and celebrated.