Periwound skin dermatitis is a common skin issue that can occur around wounds, especially in people with chronic conditions like diabetes or immobility. Periwound skin that is red, painful, and itchy signals inflammation that requires prompt periwound diagnosis and treatment to prevent interruptions in skin healing and wound closure.
As skin managers inspect the periwound skin around a wound during each dressing change, particular attention should focus on signs of damage. Causes of periwound skin dermatitis relate to excessive skin moisture, irritation from wound exudate, friction, chemical burns from wound cleansers or barrier film removers, infection risk from bacteria or fungus, and maceration from poor adhesive removal.
Holistic periwound skin assessments incorporate the patient’s risk factors, health conditions, mobility, nutritional status, and medications when interpreting skin changes to guide appropriate periwound treatment options.
Periwound Skin Assessments
A periwound skin assessment documents skin status around the entire wound perimeter, including color, texture, moisture level, intact skin, erythema, edema, warmth, and any evidence of trauma or tearing.
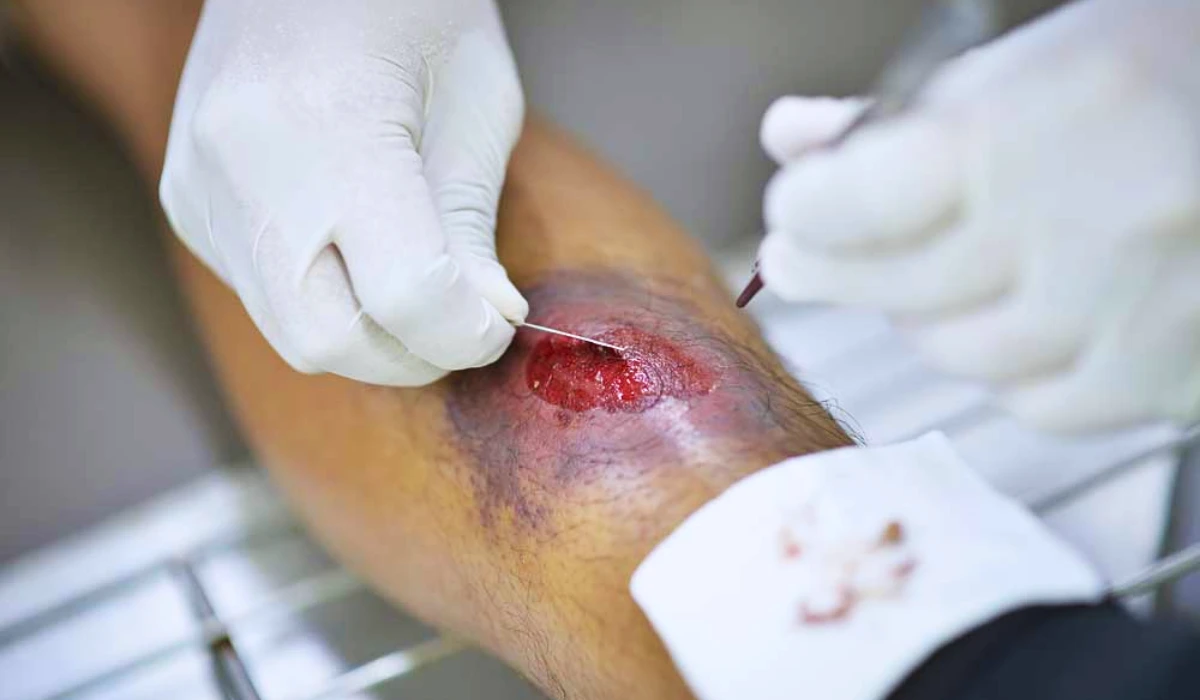
Thorough examinations occur during each dressing change to identify subtle, early periwound changes for prompt interventions before skin breakdown progresses. Photos provide visual evidence of improving or worsening.
Periwound erythema signals inflammation, presenting as red skin on lighter skin tones. In darker skin tones, the periwound presents darker than the patient’s normal skin color.
Potential periwound causes include chemical irritation, trauma from tape stripping, infection risk, fungal infection, or activating the inflammatory phase of wound healing from causes like edema or bacteria.
Causes and Treatment of Periwound Skin Changes
Appropriate periwound treatment correlates to the cause. For example, change the skin cleanser if chemical irritation occurs. Protect skin if edema or excess moisture causes inflammation.
Bacterial infections require antibiotic creams per the wound culture’s sensitivities report. Antifungal topicals treat fungal infections.
Skin maceration presents as white, soggy, peeling skin resulting from prolonged skin moisture exposure. Periwound skin requires protection from wound drainage, incontinence, perspiration, or excess moisture from hydrating wound dressings.
Appropriate periwound treatment includes skin protectants like film dressings or skin barriers applied to intact skin around the wound edge. Absorbent barrier ring dressings or oxidized cellulose dressings manage excess moisture by absorbing drainage before it contacts the skin.
An assessment for periwound skin tears or stripping evaluates wound dressing removal techniques and aging, fragile skin’s ability to tolerate tapes. Skin tears require gentle removal of any remaining adhesive using an adhesive remover wipes before cleansing.
Treatment aims to support skin healing while preventing further trauma from tape removal. Strategies include silicone tape, soft silicone foam dressings, or adhesive-free barrier film dressings.
Signs of skin damage around the periwound relate to various causes. For example, skin stripping and tears come from friction over bony prominences or aggressive adhesive removal.
Irritant contact dermatitis stems from harsh cleansers, skin barriers past their wear time, or repeated barrier film remover use. Pressure injuries develop over bony prominences when immobility prevents positional changes.
Incorporating Patient Risk Factors
Holistic periwound skin assessments incorporate the patient’s risk factors when evaluating skin changes to determine causes. Diabetes, steroid use, malnutrition, and advancing age increase infection risks, impair skin healing, and contribute to skin fragility. Immobility also prevents positional changes to redistribute pressure and allow perfusion.
Periwound fungal infections require antifungal topical treatments but also vigilance to prevent transmission or recurrence. Bacterial infections need antibiotic creams based on the wound culture’s sensitivity report. Suspected biofilm formulating in chronic wounds requires debridement to remove the barrier to healing before applying antibiotics.
Another common periwound issue comes from contact dermatitis and chemical irritation. The skin assessment documents any new products touching the patient’s skin, looking for red, painful skin with defined edges where the irritant contacted the skin.
Culprits often link to new incontinence brief brands with wetness indicators, new skin cleansers, or adhesives. Treatment involves removing the irritating product and providing symptom relief from cool compresses, low-potency topical steroids, and skin protectants.
Goals for Periwound Skin Management
Throughout assessment and treatment for periwound skin complications, the overarching goals focus on supporting wound healing momentum while preventing further skin injury or discomfort.
This requires vigilance during dressing changes to detect subtle changes early and match appropriate treatments to the cause of skin changes. Ongoing holistic reassessments ensure treatments align with the cause and evaluate effectiveness. Prevention through protection for intact periwound skin remains a priority to support wound healing.
Conclusion
Periwound skin assessments during each wound dressing change allow early detection of skin changes for prompt targeted treatment. Thorough skin inspections look for erythema suggesting inflammation and infection risks, erythema signaling early pressure injury, skin maceration from excess moisture, signs of trauma indicating skin tears or stripping, and contact dermatitis from potential irritants.
Holistic periwound assessments incorporate patient-centered factors to identify risks for skin complications and guide appropriate treatment options when skin changes occur. The goal focuses on supporting wound healing momentum while preventing further skin damage or Patient discomfort through diligent assessments and prompt treatment customized to address the cause of skin changes.
What prevention strategies might help reduce periwound skin risks for patients with chronic, non-healing wounds?

