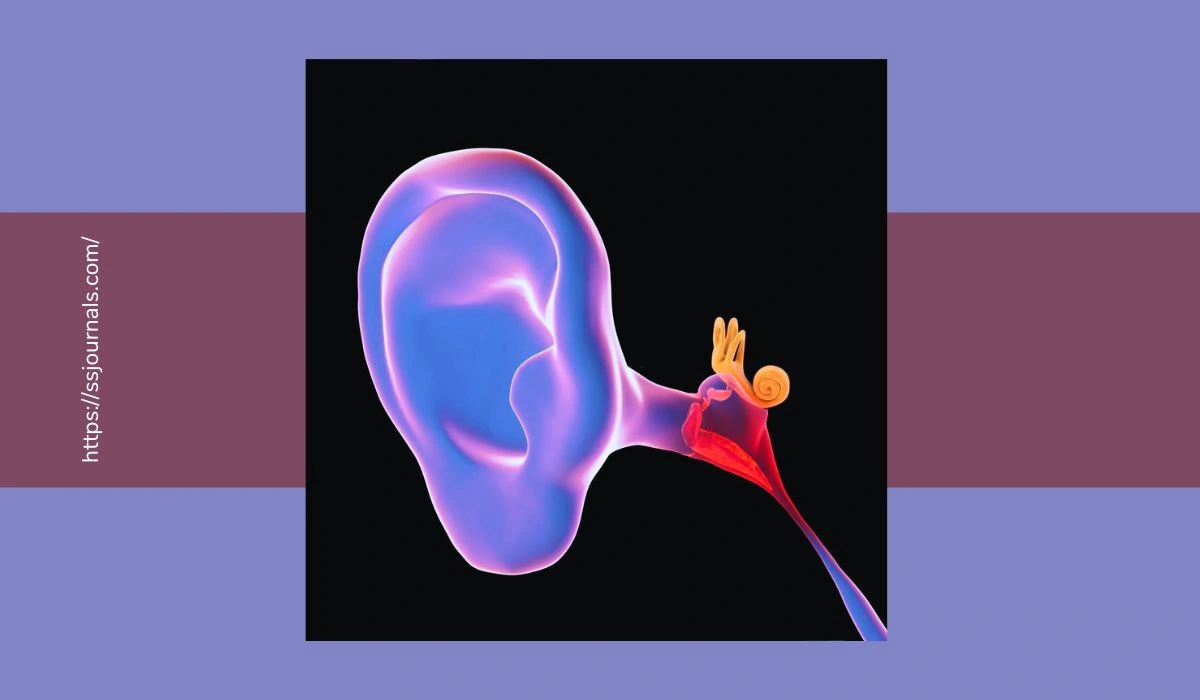
There are three components to the ear. The eardrum canal and the visible portion of the ear are included in the outer ear.
The outer ear, which contains tiny bones that amplify sound, is separated from the inner ear by the eardrum.
Sounds are converted into electrical impulses in the inner ear, transmitting those signals to the brain.
The middle ear is meant to have good ventilation from the air that often rises from behind the nose through the Eustachian tube, keeping it dry and clean.
The middle ear becomes wet and warm, which is an ideal environment for the growth of bacteria when there is insufficient fresh air ventilating the area, as occurs when the Eustachian tube is blocked. This causes ear infections.
What Are The Causes?
Bacterial or viral infections can cause ear infections. They can concern your outer ear, inner ear, and middle ear.

They often go away on their own, but they occasionally hurt due to swelling or fluid buildup. Acute and chronic forms of ear infections exist.
Even though the brief, acute ear infections hurt. Chronic ear infections are not frequent. Although damage to the inner and middle ear is possible, it is usually not permanent.
An upper respiratory viral infection, such as the flu or a cold, is the most typical cause of an Ear health infection in children. These conditions can cause the Eustachian tube to swell so air cannot enter the middle ear.
Allergies, including those to pollen, dust, animal dander, or food, as well as smoke, fumes, and other environmental toxins, can have the same impact as a cold or the flu.
Although bacteria can directly cause an ear infection, they typically follow a viral infection or an allergic reaction and swiftly make their way into the warm, wet environment of the middle ear.
Invading germs can cause severe damage by turning inflammation into an infection and elevating the body’s temperature.
The bacteria that cause many cases of sinusitis, pneumonia, and other respiratory infections are among those most frequently discovered in infected middle ears.
The conjugate pneumococcal vaccine, according to studies, is particularly efficient against several strains of the most typical bacteria that cause ear infections.
This vaccination is frequently administered to newborns and young children to prevent meningitis, pneumonia, and blood infections.
What Signs Indicate An Ear Infection?
Common symptoms of an ear infection include:
- a persistent pressure within your ear that feels mildly uncomfortable
- pus-like ear discharge
- hearing loss
These signs may be recurring or intermittent. It’s possible for both ears to be affected at once.
When both ears are infected, the result is a painful condition known as a double ear infection. Chronic ear infections often have less obvious symptoms than their acute counterparts.
Symptoms Of Ear Infection In Infants
Young infants and babies may reveal auxiliary symptoms of an ear ailment in addition to those seen in adults, including:
- straining or rubbing their ears
- fever
- not responding to particular noises
- losing balance frequently
- headache, fussiness, or agitation
- reduced appetite
Ear infections typically last fewer than three days but may extend up to a week.
How Can I Avoid Getting An Ear Infection?
You must eliminate as many environmental pollutants as possible in your house. These include:
- Dust
- solvents and cleaning agents
- cigarette smoke
- Control your allergies and limit your or your child’s exposure to sick people.
Some, but not all, cases of ear infections can be avoided by taking precautions against colds, the flu, and other ailments. Here are a few essential measures to take:
- Make sure to acquire the recommended vaccinations for everyone in your home, including your kids, at the appropriate times. Flu and pneumococcal vaccines are included in this.
- Make washing your hands a family ritual and a habit.
- Avoid group care if feasible, especially during the flu season.
- It is preferable to breastfeed your baby for the first 6 to 12 months, if feasible, to prevent ear infections because newborns who are fed formula are more likely to have ear infections.
You can easily prevent ear infections among adults and children by being careful. However, do seek medical help when the symptoms are severe.