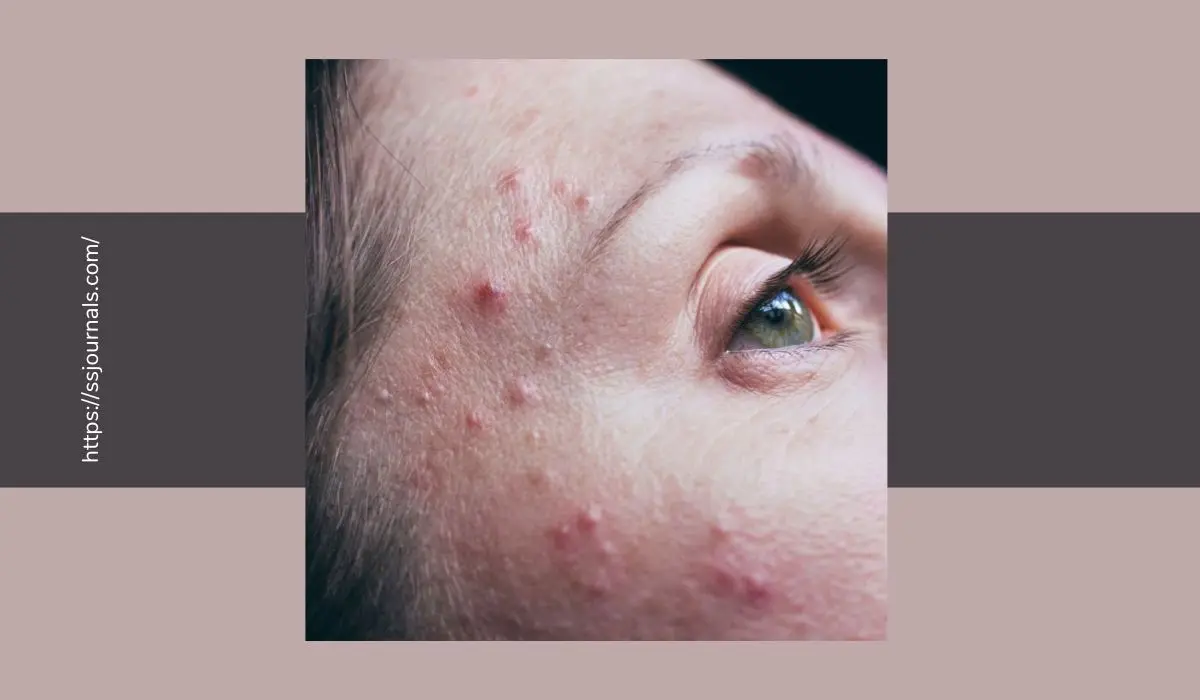
Basal Cell Carcinoma is a sneaky type of skin cancer that comes from the lowest layer of the epidermis.
It usually grows slowly, but can be dangerous if not treated.
Sunlight or tanning beds cause this condition, and those with fair skin, a family history of skin cancer, and a weakened immune system are more likely to get it.
The signs of Basal Cell Carcinoma vary. It could show up as a pearly bump, a flat scar-like lesion, an open sore that won’t heal, a red patch, or a transparent bump with blood vessels.
Knowledge is power when it comes to Basal Cell Carcinoma.
Protect your skin with sunblock with a high SPF, protective clothing, shade when the sun is strongest, and no tanning beds.
Self-examination and regular visits to a dermatologist will help catch this skin cancer early.
Understanding Basal Cell Carcinoma
To understand basal cell carcinoma, delve into its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Begin with knowing what basal cell carcinoma is and the specific factors that can lead to its development.
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is a skin cancer that starts in the deepest layer of the epidermis. It’s like a sneaky burglar that breaks into your skin without asking for permission.
UV radiation from sunlight or tanning beds can cause it. Fair skin, sunburns, a family history of skin cancer, and too much UV exposure can put you at risk.
It’s usually a small, waxy bump or a pinkish patch that may bleed or crust over.
BCC can cause damage and disfigurement if left untreated for too long.
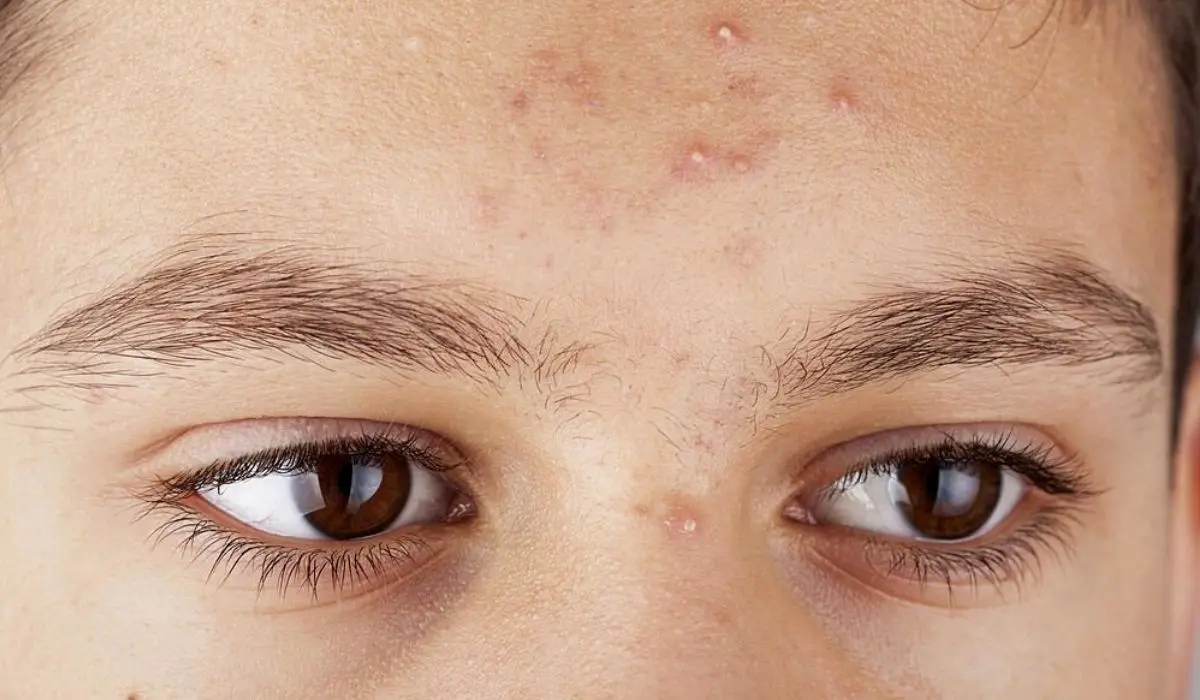
But it’s not usually life-threatening, like melanoma. Early detection and treatment are essential though.
Treatments include surgery, Mohs surgery, cryosurgery, radiation, topical meds, and photodynamic therapy.
Causes Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma, the most common type of skin cancer, has multiple causes.
Excessive and unprotected exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is a major factor.
Other risk factors include fair skin, a history of sunburns, exposure to chemicals like arsenic, and a weakened immune system.
UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to uncontrolled growth and the formation of tumors.
Fair-skinned people are more vulnerable due to less melanin, which acts as natural protection from the sun. Severe sunburns also raise the risk of developing cancer.
Substances like arsenic in drinking water, coal tar, and creosote can increase the risk too.
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or on immunosuppressants after an organ transplant, are also at a higher risk.
Recognizing The Symptoms
To recognize the symptoms of basal cell carcinoma and determine whether medical attention is necessary, familiarize yourself with common indicators.
Common symptoms of basal cell carcinoma include [sub-section 1] and knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial for timely treatment.
Common Symptoms of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a common type of skin cancer with certain signs. Look out for these:
- Ulceration: A sore or ulcer that won’t heal after weeks.
- Bleeding: Unexplained bleeding from a lesion.
- Texture: Rough, scaly patches.
These symptoms may differ based on the cancer’s stage and location. If you spot something strange about your skin, see a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis.
When To Seek Medical Attention
It’s key to know when to get medical help for your health. If ignored, symptoms can lead to bad things. So, be aware of the red flags that mean you need treatment.
If your symptoms stay or get worse, check with a healthcare pro.
Troubles that require urgent attention include: severe pain, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, bleeding that won’t stop, and passing out. These could show an underlying condition.
High fever is a sign of infection and can point to something serious. Get medical help right away so the cause can be found and treated.
Also, if you have sudden changes like unexplained weight loss, lumps or bumps, or big changes to your bowel or bladder habits, you must see a doctor. These could be signs of serious illnesses like cancer or hormonal trouble.
To get the right treatment on time:
- Listen to your intuition: if something feels off, don’t wait to ask for advice.
- Write down your symptoms: jot down any new or recurring problems to give your healthcare provider accurate info.
- Ask for help: tell someone you trust about your worries for emotional support.
- Get regular check-ups: screenings can help spot potential health issues early.
- Learn about different medical conditions: so you can recognize signs and symptoms quickly.
It’s vital to get medical help at the right time. Looking after your health should be your top priority – never underestimate the power of early intervention.
Treatment Options
To effectively address various treatment options for basal cell carcinoma, such as surgical procedures, non-surgical treatments, and potential side effects and risks, you need to understand the available solutions.
These sub-sections will give you a concise overview of the different approaches without any unnecessary fluff or explanations.
Surgical Procedures for Basal Cell Carcinoma
Surgically treat Basal Cell Carcinoma (a type of skin cancer), with these options:<\p>
- Excision: Cut out the tumor plus surrounding healthy tissue. Ensures cancer cells’ removal.
- Mohs surgery: Peel away tumor layers, one by one. Check each layer for cancer under a microscope. High success rate, preserves healthy tissue.
- Cryosurgery: Use liquid nitrogen to freeze & destroy tumors. Works best for small, superficial cases.
- Curettage & electrodesiccation: Scrape off tumor using curette. Electrodessication eliminates remaining cancer cells.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments offer many advantages, including shortened recovery times and reduced risk of complications. These treatments vary, such as:
- injections
- laser therapy
- radiofrequency ablation
- oral medications
- topical creams/patches
- physical therapy
- acupuncture
- herbal remedies
- lifestyle modifications
Read More:- What Does Kokum Butter Do For The Skin? What Are The Benefits?
Tips For Preventing Basal Cell Carcinoma
Skin cancer is a serious and dangerous disease, but prevention is possible. Here’s how to reduce your risk of developing basal cell carcinoma:
- Protect yourself from the sun: Wear protective clothing like long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses. Also, avoid the sun between 10 am and 4 pm.
- Apply sunscreen regularly: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Seek shade: Find shade under trees, umbrellas, or other structures when outdoors to minimize exposure to direct sunlight.
- Avoid tanning beds: Artificial UV radiation emitted by tanning beds can cause skin cell damage and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Check your skin regularly: Perform regular self-examinations and check for any changes in moles, spots, or other abnormalities. If you notice something suspicious, see a dermatologist.
Conclusion
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that starts in the basal cells of the epidermis. Prolonged UV radiation exposure from sunlight or tanning beds can cause it.
Common signs include open sores, red patches, shiny bumps, and scars for no reason.
If found early, various treatments like surgery, cryotherapy, topical meds, and radiation can effectively manage and remove it.
Prevention is key. Wear protective clothes, use sunscreen with high SPF, avoid peak sunlight hours, and do regular skin checks.
By understanding basal cell carcinoma causes, symptoms, and treatments, we can fight it. Early detection and education on healthy skin practices will help keep us safe from this dangerous condition.