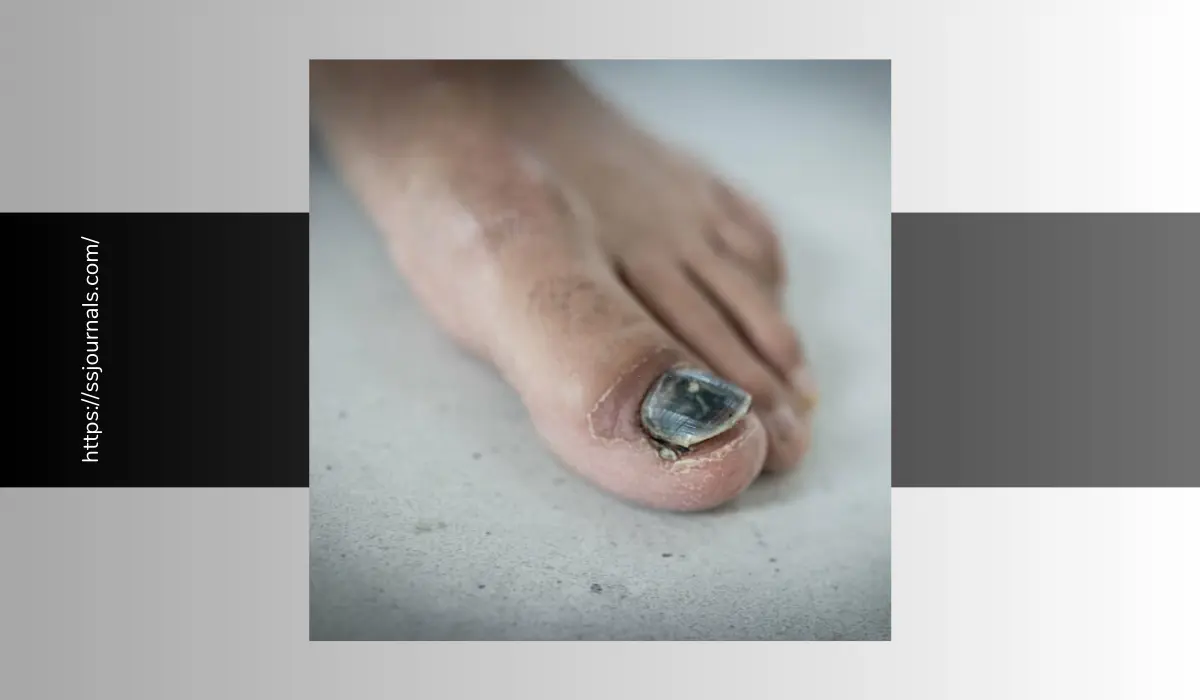
Black toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection of the toenails that causes the nail to become discolored, thickened, and brittle. It typically begins as a white or yellow spot under the tip of the toenail and gradually spreads, causing the nail to turn dark brown, black, or yellow.
Black toenail fungus affects around 10% of the population and is more common in older adults. If left untreated, the infection can spread to other toenails and persist for years. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available to get rid of black toenail fungus.
What Is Black Toenail Fungus?
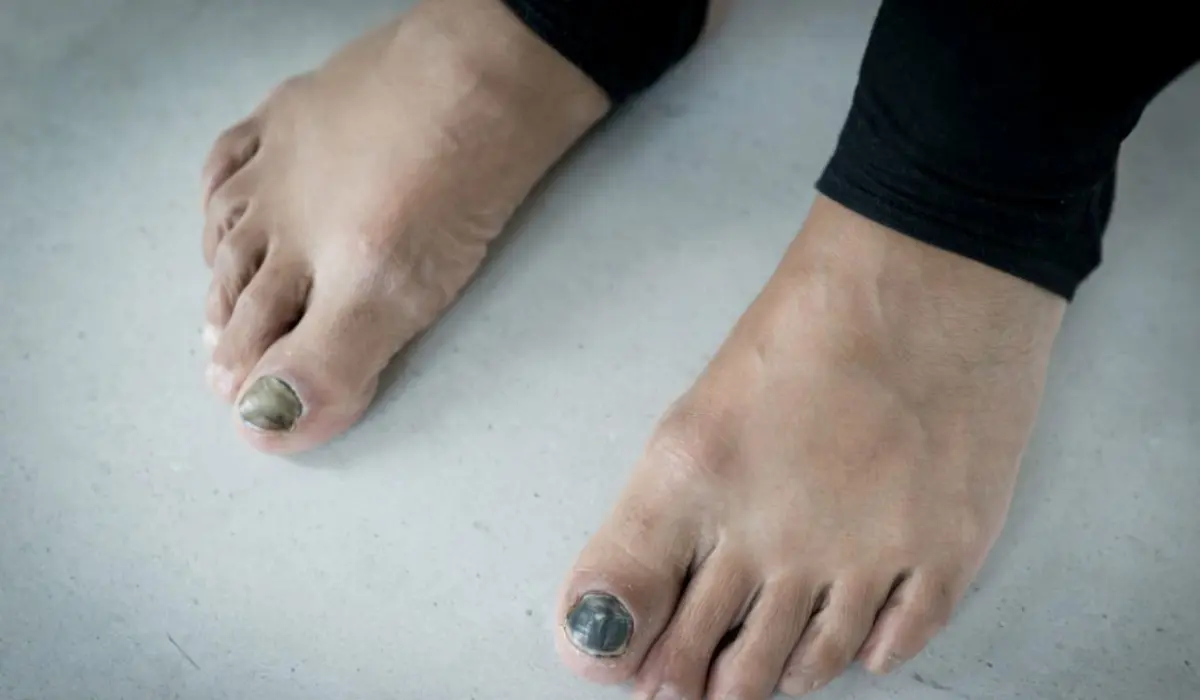

Onychomycosis, or black toenail fungus, is a fungal infection of the toenail caused by dermatophyte fungi, such as Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. These microscopic organisms thrive in warm, moist environments like showers, pools, and inside shoes.
Once the fungus gets under the nail, it begins to grow, damaging the nail bed and causing the nail to appear dark, distorted, and crumbly. In severe cases, the toenail may thicken, lift up from the nail bed, and eventually fall off. Black toenail fungus commonly affects the big toe but can also spread to other toenails. If left untreated, the infection may persist for years.
Signs Of Toenail Fungal Infection
There are several distinct signs that point to a fungal infection of the toenail:
| Discoloration | The nail appears yellow, brown, or black. The darker color is debris accumulating under the nail. |
| Thickening and crumbling | The nail becomes abnormally thick and brittle, with debris accumulating underneath. Pieces of the nail may chip off. |
| Distortion in shape | The infected part of the nail loses its normal shape. The toenail may separate from the nail bed. |
| White or yellow streaks | streaks or dots appear on the nail near the tip. This is early fungal growth under the nail. |
| Odor | In severe cases, a foul odor may accompany the infection. |
What Causes Black Toenails?
There are several risk factors that can cause a fungal toenail infection:
- Exposure to humid public areas (gyms, showers, pools)
- Sweaty feet provide a moist environment where fungi thrive.
- Injuries to the nail or skin make it easier for fungi to enter.
- Reduced blood circulation is more common in the elderly.
- Weakened immune system; certain illnesses and medications
- The use of occlusive footwear prevents ventilation and drying of feet.
- History of an athlete’s foot can spread to toenails
Walking barefoot in warm, damp areas like pools, showers, or locker rooms can expose feet to the fungi that cause black toenail fungus. People with chronic diseases like diabetes or a weakened immune system are at higher risk.
How To Get Rid Of Black Toenail Fungus?
Fortunately, prompt treatment can cure most cases of black toenail fungus. Treatment options include:
Prescription oral antifungal medications: Itraconazole or terbinafine tablets taken for 6 to 12 weeks. prescription topical antifungal lacquers applied directly to nails for 48 weeks.
Laser therapy: low-level laser beams help eliminate fungus. Requires multiple sessions.
Removal of an infected nail: Part or all of the nail is surgically removed to eradicate infection. New nails regrow.
Keeping feet clean and dry can help prevent recurrence. Wearing flip-flops in public showers, avoiding tight shoes, and treating athletes’ feet also reduce the risk of reinfection.
See a podiatrist or dermatologist at the first sign of black toenail fungus for proper diagnosis and treatment. Leaving it untreated allows the infection to worsen over time.
Bottom Line
Black toenail fungus, or onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection, especially in older adults. It causes the toenail to become discolored, thick, brittle, and distorted in shape. Trichophyton fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and infect the nail bed.
Without treatment, the infection worsens progressively and can spread to other nails. Oral medications, medicated nail lacquers, laser therapy, and nail removal are effective treatments.
Preventive measures like wearing shower shoes in public areas, keeping feet clean and dry, and treating athletes’ feet are crucial to avoiding recurrent infections. At the first sign of black toenail fungus, see a podiatrist for a proper diagnosis and prompt treatment.