Ulcerative colitis (UC) could be a condition that influences millions of people globally, bringing with it diligent irritation within the stomach-related framework. One charming perspective of this confusion is the relationship between smoking and UC. In this article, we’ll investigate this inquisitive association and what might be cruel for those living with UC.
Understanding Ulcerative Colitis
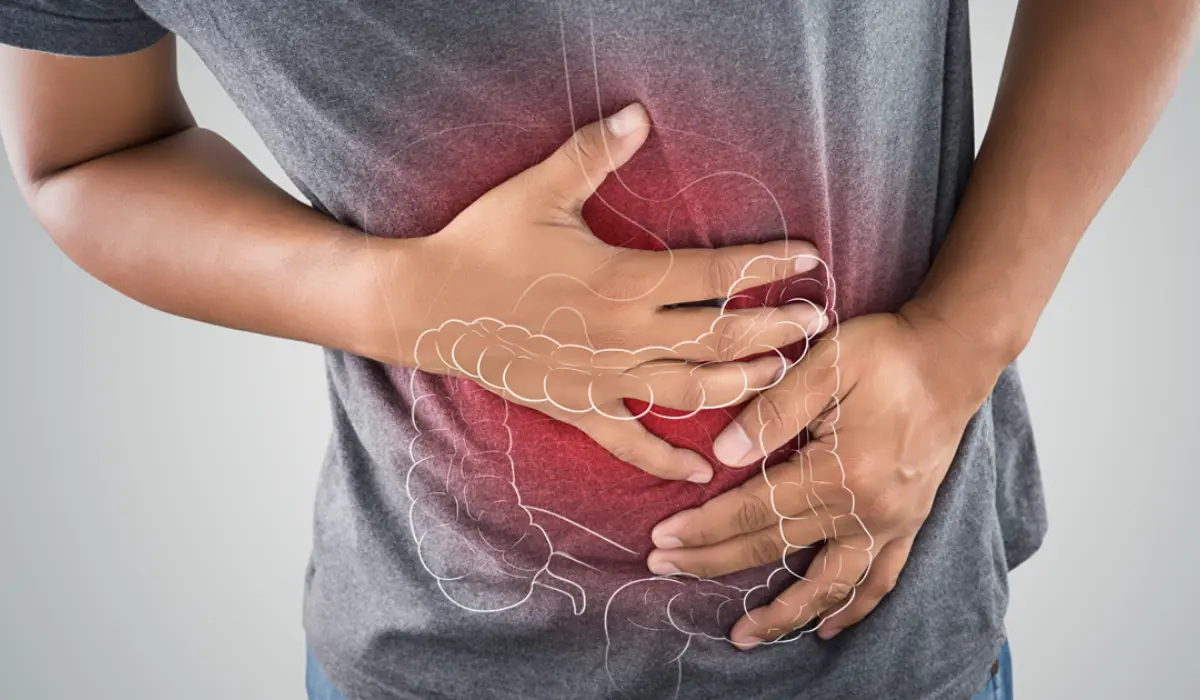
First, let’s get to know UC a bit better. It’s the shape of an incendiary bowel malady (IBD) that primarily impacts the colon and rectum. The trademark of UC is persistent irritation and ulcers within the internal lining of the stomach-related tract, leading to side effects like paunch torment, visit trips to the restroom, rectal dying, and unintended weight misfortune. Even though we’re not beyond any doubt what triggers UC, it’s accepted to include a blend of hereditary, natural, and resistant framework factors.
The Riddle Of Smoking And Ulcerative Colitis
Research has shed light on the complex and to some degree puzzling relationship between smoking and UC. This charming connection has been investigated in various ways, however, it’s significant to note that the association remains to some degree slippery, with personal encounters changing significantly.
Diminished Hazard in Smokers: It might sound outlandish, but a few consider reliably proposing that current smokers confront a lower hazard of creating UC compared to non-smokers. This chance lessening is more recognizable in those who as of now smoke than in previous smokers.
Expanded Seriousness in Set up UC: Be that as it may, the story takes a turn when it comes to people who as of now have UC. Smokers with UC tend to involve more severe indications, more visit backslides, and a hoisted chance of complications compared to non-smokers with UC.
Potential Impact on Pharmaceutical Reaction: Smoking may also affect how people with UC react to certain medicines. For occurrence, a few things propose that smokers with UC may react superior to corticosteroids but not as well to anti-TNF (tumor rot figure) drugs commonly utilized to treat irritation in UC.
Peeling Back The Layers: What’s Happening?
So, what could be going on underneath the surface of the smoking-UC connection? Analysts have put forward a few potential explanations. This may well be a reason why smoking shows up to diminish the chance of creating UC.
Intestine Microbiota Changes: Smoking can cause shifts within the composition of the intestine microbiota. These minor life forms are vital in keeping up intestine well-being and impacting the resistant framework. Changes in intestine microbiota can contribute to the expanded illness seriousness in built-up UC among smokers.
Resistant Framework Changes: Smoking is known to impact the safe framework. Be that as it may, the precise instruments by which this happens and how it impacts the improvement and movement of UC are not completely understood.
The Huge Picture: Clinical Implications
The complicated relationship between smoking and UC holds imperative clinical implications:
Smoking Cessation: If you have UC and you smoke, it’s significant to prioritize stopping. The well-being risks linked to smoking are considerable, and any potential benefits for UC do not exceed the hurt caused by tobacco use. Center on smoking cessation as the best priority.
Observing and Instruction: Normal observing of malady movement and teaching patients the potential effect of smoking on their condition are essential. Healthcare suppliers play a key part in making a difference in patients’ making educated choices concerning their treatment and way of life choices.
Investigating Elective Treatments: Continuous investigation points to elective treatments and drugs that might duplicate the potential benefits of nicotine without the destructive impacts of smoking. These medications may give a more secure and more viable approach to overseeing UC.
Conclusion
The association between smoking and ulcerative colitis is complex and multifaceted. Whereas it may show that smoking diminishes the hazard of creating UC, it’s not a prescribed methodology for illness anticipation due to the various well-being dangers connected to smoking. For people now analyzed with UC, smoking can compound the seriousness of the disease and its complications.
If you have got ulcerative colitis, dodge taking up smoking as a implies of managing your condition. Work closely with your healthcare suppliers to make a personalized treatment arrangement that considers your needs and hazard variables. Quitting smoking is exceedingly suggested for general well-being, and there are different non-smoking procedures accessible for overseeing UC effectively.
As inquiries about this range proceed, we trust to pick up distant better a much better a higher an improved a much better understanding of the complex relationship between smoking and UC. Whereas the association between the two is still confusing, it emphasizes the significance of personalized care and an all-encompassing approach to overseeing this challenging condition.
FAQ
No, there isn’t a straightforward answer. While research suggests a complex relationship, the connection between smoking and UC is not fully understood. Smoking appears to reduce the risk of developing UC but can worsen the disease’s severity in those who already have it.
Smoking does seem to reduce the risk of developing UC, but it’s not a recommended strategy for prevention. The serious health risks associated with smoking far outweigh any potential benefits for UC.
It’s unclear, but one theory is that smoking may cause changes in the gut microbiota and the immune system, making the disease more severe in smokers with UC.
Absolutely. Quitting smoking is highly recommended for overall health, even for those with UC. While it might lead to some temporary worsening of symptoms, the long-term benefits of quitting smoking far outweigh any short-term issues.
Researchers are exploring alternative therapies and medications that aim to provide the potential benefits of smoking (such as anti-inflammatory effects) without harmful side effects. However, these are still under investigation and not widely used in clinical practice.

