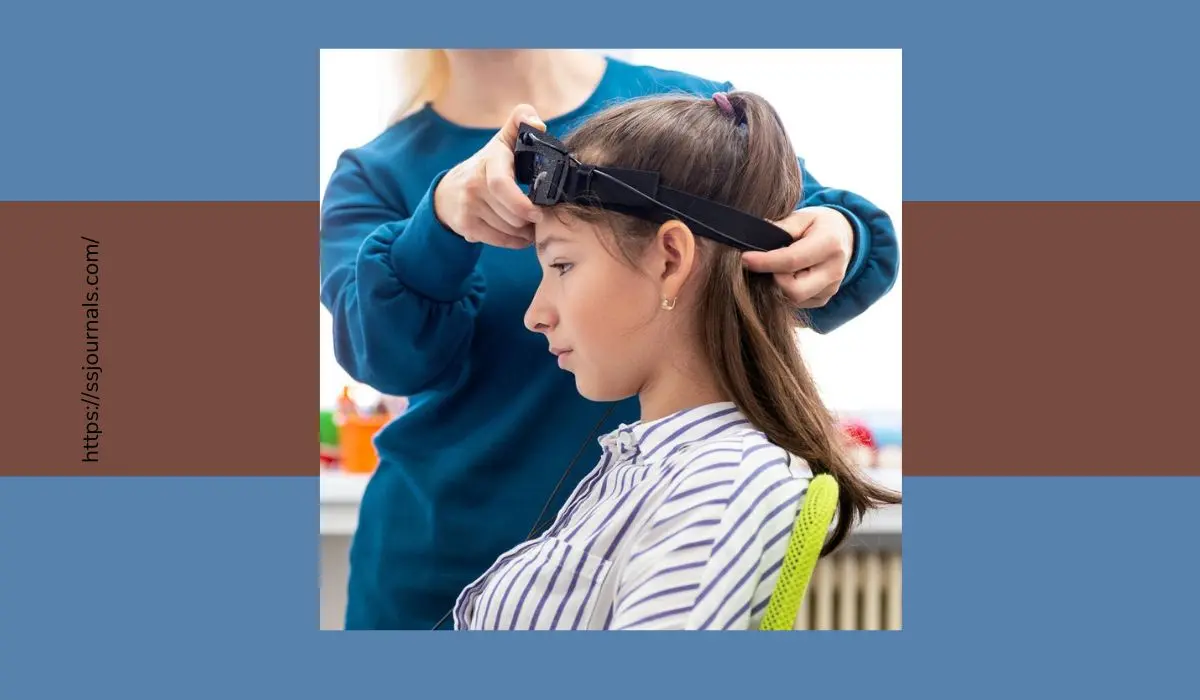
Neurotherapy refers to a set of techniques and treatments aimed at improving brain health and function using non-invasive methods to modulate brain activity. Neurotherapy harnesses the power of neuroplasticity – the ability of the brain to reorganize and adapt both functionally and physically throughout our lives.
The main approaches used in Neurotherapy include neurofeedback, transcranial magnetic stimulation, cognitive training exercises, and brain stimulation through electrical or magnetic means.
These therapies show promise in enhancing cognitive skills, treating mental health conditions, managing pain, and optimizing brain performance.
What Is Neurotherapy?
Neurotherapy involves techniques that seek to improve the brain’s capabilities by directly training cognitive skills or by influencing brainwave patterns and activity in beneficial ways.
The goals of neurotherapy include:
- Enhancing focus, attention, memory and overall cognitive performance
- Managing conditions like ADHD, anxiety, depression, addictions, OCD, PTSD and insomnia
- Improving rehabilitation and function after brain injuries or neurological illness
- Controlling pain symptoms and severity
- Optimizing brain health and cognitive functioning as we age
Neurotherapy techniques are non-invasive and work by leveraging our brain plasticity – the ability of our neural connections and circuits to change and adapt in response to stimulation and experience even into adulthood. This allows for new patterns of brain activity that can alter behaviors, emotions, pain perception, motor skills and more.
Major Neurotherapy Approaches
Some of the most common current neurotherapy approaches include:
➜ Neurofeedback
Using electroencephalography (EEG) to provide visual or auditory feedback about real-time measures of brainwave activity. Allows self-regulation of brainwave patterns.
➜ Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
Focal stimulation of the brain through electromagnetic induction. Can excite or inhibit activity in targeted regions.
➜ Cognitive training
Structured practice on tasks that enhance particular cognitive skills such as memory, attention, processing speed, and problem-solving.
➜ Biofeedback
Uses physiological signal feedback like EEG, heart rate, or skin temperature to teach self-regulation of bodily processes impacted by the brain.
➜ Electrical brain stimulation
Techniques like deep brain stimulation (DBS), transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES), and others use electrical currents to modulate brain regions.
➜ Magnetic brain stimulation
Repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation or magnetic seizure therapy uses magnetic fields to induce electrical changes in the brain.
➜ Computerized cognitive training
Structured cognitive skill practice and games are driven by algorithms that adapt to performance.
These therapies leverage our brain’s innate potential for neuroplastic change. Regular training can induce long-term changes in neural pathways, chemistry, and connectivity.
Related: How To Stop Brain Zaps From Anxiety? Solution For Anxious Mind
Key Applications Of Neurotherapy
Some of the main conditions and outcomes shown to benefit from neurotherapy techniques include:
ADHD
Neurofeedback training helps regulate beta and theta brainwave activity associated with ADHD symptoms of impulsivity and inattention. Studies report neurofeedback can improve attention, hyperactivity, cognition, and behaviors.
Anxiety and Depression
Regulating alpha and theta brainwave activity via neurofeedback may have anti-anxiety and antidepressant effects. TMS also shows efficacy as therapy for depression.
Addictions
Both neurofeedback and tDCS applied to frontal and limbic brain regions have been shown in studies to reduce cravings, consumption, and relapse rates in substance addiction.
Insomnia
Neurofeedback that enhances theta waves and reduces high-frequency beta waves may improve sleep quality and duration.
Chronic Pain
Reduced pain perception has been demonstrated from neurofeedback, tDCS, CES, and TMS due to modulation in areas of the brain involved in pain processing.
Cognitive Decline
Cognitive training focusing on memory, attention, speed, and problem-solving can improve performance on these tasks and even translate to better function in daily life.
Brain Injury Rehabilitation
Stimulating neuroplasticity through techniques like cognitive training, tDCS and TMS has been shown to improve motor and cognitive recovery after stroke and traumatic brain injury.
The unique advantage of neurotherapy is the ability to directly influence brain regions and activity patterns associated with undesirable symptoms or needed skills. The brain’s plasticity allows for new, beneficial connections and signaling.
How Effective Is Neurotherapy?
The level of evidence, efficacy and long-term benefits of neurotherapy varies across the different techniques and applications. However, clinical studies provide ample support for many uses.
For ADHD, ADD and anxiety, neurofeedback has good evidence with demonstrated behavioral, cognitive and mood improvements versus control groups. The effects can last months after treatment cessation.
Research supports cognitive training for boosting focused skills like memory and attention in both healthy and cognitively impaired adults. Generalization of daily function is still limited.
For depression, TMS applied to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex shows response and remission rates comparable to medication and longer-lasting effects.
Pain reduction from noninvasive brain stimulation like tDCS is small but can be meaningful for chronic pain, with good evidence. Combining with other pain therapies is the most effective.
While protocols and outcomes are still being optimized in many areas, neurotherapy shows promise for recalcitrant neurological and psychiatric conditions. It provides an adjunct or alternative to medication or psychotherapy. As brain science and technologies evolve, neurotherapy is poised to transform how we enhance and heal the brain.
Conclusion
The diverse techniques of neurotherapy leverage neuroplasticity to help strengthen cognitive skills, manage psychiatric symptoms, rehabilitate brain function, and even change pain perception.
Noninvasive techniques like neurofeedback training, transcranial brain stimulation, cognitive exercises, and other modalities can improve uncontrolled brainwave patterns, alter neural connectivity through stimulation, and drive beneficial neuroplastic adaptations through rigorous skill training.
While more research is still needed, current evidence supports the use of neurotherapy for conditions including ADHD, anxiety, depression, addictions, insomnia, cognitive decline after brain injury, chronic pain, and more.
Ongoing innovations in neuroscience, biofeedback, electrical stimulation, computerized training, and other technologies will continue to enhance the applications of neurotherapy and its position as an important route to brain optimization.
More: Emerging Brain Technology In Behavioral Health – Importance

